

Did You Know?
We serve loans, the best way you can borrow

We serve loans, the best way you can borrow

For small businesses, delays, paperwork, and high costs often block the way. Debt financing gives a fast and simple option. It helps raise funds without giving up ownership. What is debt financing? Find out more here.
With easy terms and fixed repayments, debt financing solves funding problems while supporting business needs (such as emergencies or daily expenses).
The debt financing meaning is borrowing money to run or grow a business. A company takes a loan and agrees to repay it with interest. It is different from raising money by selling shares, where ownership gets divided. It works well for companies that want full control but need funds for short or long-term use. An instant personal loan is one such option that offers quick access to capital. It offers clear repayment plans, making it easier to manage costs. This funding method helps solve urgent financial problems without giving up any part of the business or involving outside investors.

A few types of debt financing are mentioned below. Each has a specific purpose depending on risk & security.
1. Unsecured Business Loans - These loans do not need security. Lenders check credit score and income. Businesses with strong profiles use this option for speedy access to short-term funds.
2. Secured Business Loans - These loans require assets as security. If the loan is unpaid, lenders can claim the asset. It helps get bigger amounts at lower interest rates.
3. Small Business Loans - These loans are made for small firms with simple needs. They cover daily expenses or minor upgrades.
4. Equipment loans - This loan helps buy tools or machines for business. It is for firms that want to upgrade their operations with new equipment.
Learn how does debt financing work below.
According to the characteristics of debt finance, it starts when a business applies for a loan from a lender. After checking income, credit score, and documents, the loan is approved. The company receives money & agrees to pay back the amount in fixed parts. These payments include interest (which is the cost of borrowing). In some cases, a debt consolidation loan may also be considered to streamline multiple repayments into one.
Terms depend on the loan type & the borrower's profile. Repayment is usually monthly. Missing payments may result in additional fees or a lower credit score. A few may opt for equal instalments or balloon payments (where the maximum of the principal amount is paid at the term's end).
Read also about: Debt to Income Ratio

One advantage of debt financing is the lower tax expenses. Interest paid on loans can reduce taxable income. This helps save money during tax season & makes borrowing more affordable for growing businesses.
The other advantages of debt financing are fixed & easy expense monitoring. Fixed repayments help plan cash flow better. Businesses can track income & spending.
Owners do not give away any part of the business. Decisions stay in their hands, keeping control while still getting the money needed. But if the terms mention, the lender may decide to ask what the money will be used (for instance, equipment loans).
Loan repayments are due on time, with interest added. Even during tough times or losses, the business must keep paying regularly without delay.
There are negative effects of debt financing. Late or missed payments may reduce the credit score. It limits forthcoming loan opportunities or, at times, raises the cost of borrowing.
Unlike the benefits of debt financing, loan interest rates may stay high for some businesses. Rates depend on income, credit score, and the lender's risk check.
The company pays the interest alongside the principal amount to the lender. This interest payment is known as a coupon payment. It represents the cost of debt. The dividend payments, on the other hand, made to the shareholders are the cost of equity. The cost of equity & cost of debt is called the cost of capital when combined.
It is the decision of the company that ensures a higher return than the cost of debt. The company otherwise would not be able to succeed for lenders, but still needs to pay them & go into the loss.
So, the company has to consider:
Cost of Capital (Cost of Debt plus cost of equity).
If the company pays late or misses one payment, extra charges apply. Debt financing costs should be checked fully before agreeing.
Here's one of the debt financing examples. Company X runs a small textile business in Pune. It needed funds to buy new machines and manage seasonal stock. The company chose debt financing to avoid giving up any ownership.
Loan Amount & Interest:
It borrowed ₹2,00,000 at an interest rate of 18% per year.
Term:
The loan term was 18 months with monthly repayments.
Repayment:
The repayment schedule required paying ₹12,000 each month. It covers both principal as well as interest.
This plan helped Company X grow without delay. The loan covered costs quickly and was easy to manage. Since the payments were fixed, it was simple to plan monthly budgets. Debt financing gave them funds without stress or loss of control.
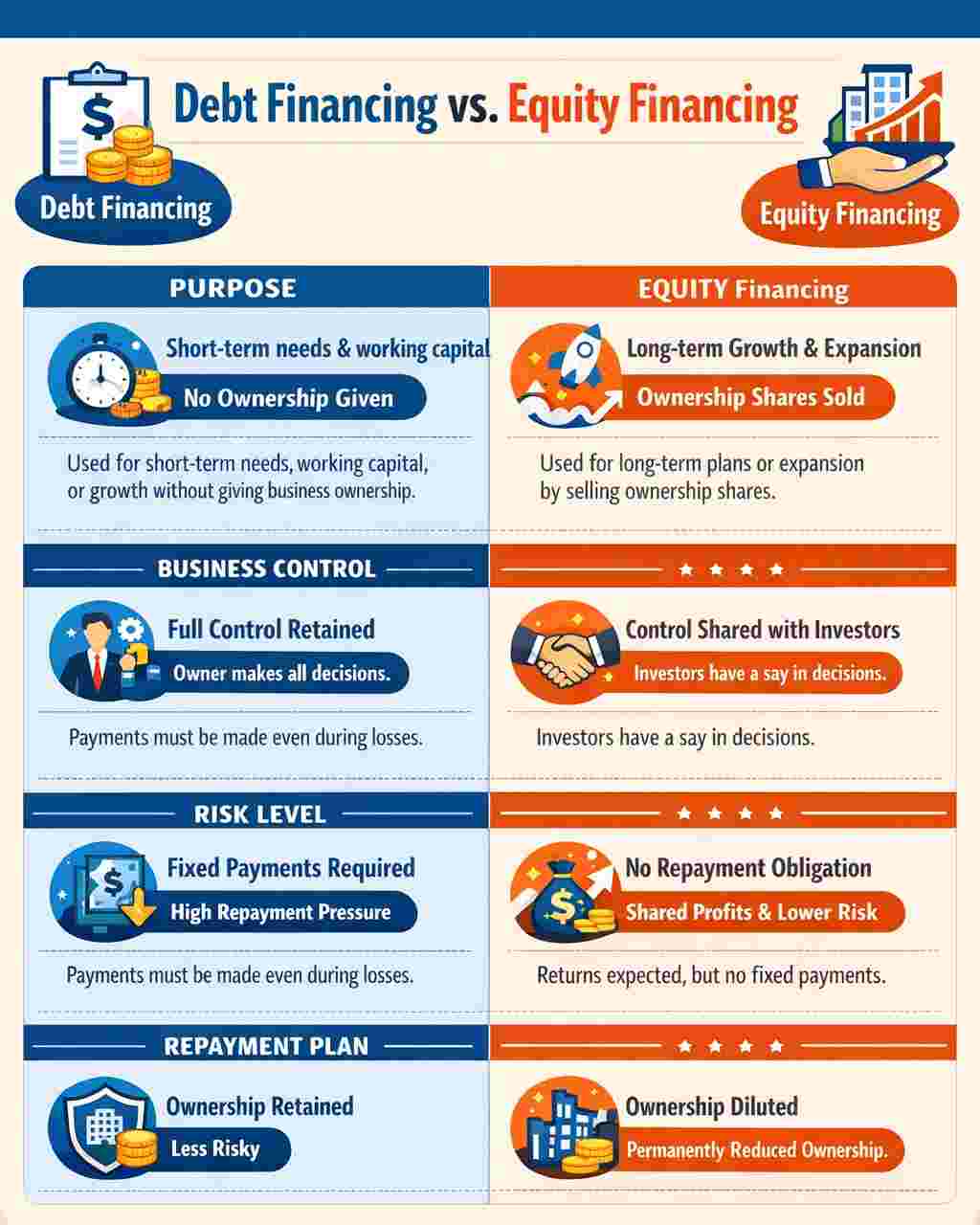
| Aspect | Debt Financing | Equity Financing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Used for short-term needs, working capital, or growth without giving business ownership over a mutually agreed tenure | Used for long-term plans or expansion without repayment pressure by selling ownership shares to any external investor |
| Business Control | The owner keeps full control and makes all decisions independently. | The owner gives up part of the control as investors gain a say in business matters. |
| Risk Level | Fixed payments add pressure even during losses or months when income is low. | No repayment pressure unless the company is liquidated or sold. Investors share profits and may expect returns. |
| Repayment Plan | Less risky as ownership of the company is retained | Riskier as earnings are shared and ownership is permanently reduced. |
| Category | Debt Financing | Interest Rates |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Borrowed money is used to grow or support the business. | Extra money is paid for using someone else's money. |
| Investor Expectation | Lenders expect timely payments along with fair interest. | Higher rates bring better returns but show more risk. |
| Cost Dynamics | Depends on the loan term, credit score, and charges. | Changes with market, credit score, and repayment history. |
| Tax Impact | Interest cuts taxable income, saving money legally. | Does not lower taxes but affects total loan expense. |
| Risk Consideration | More debt raises pressure and limits future borrowing. | A higher rate shows that the lender feels more risk is involved. |
| Strategic Impact | Helps meet goals if repayment fits business income. | Impacts loan choice and financial planning. |
So, debt financing helps solve urgent money needs without giving away control. It offers quick access to funds with simple terms and fixed payments. Businesses can manage costs, grow fast, and plan better. But loans come with interest and risks if not paid on time.
Check all charges & repayment terms clearly before choosing a loan. Select a loan that suits your income & purpose. Debt financing works when considered smartly with clear goals.
Debt financing is money borrowed and paid back with interest. Equity financing involves raising capital by offering a share in your business. If you prefer to retain full ownership and can manage regular payments, debt financing is suitable. Equity may be great if you are in the early stage and open to sharing control.
Lenders look at your credit score & income stability. They also check current debts alongside repayment history. An income & strong bank records (with a clear repayment plan) may improve your chances. Collateral, if needed, also plays a role. Business size, purpose of loan, and documents provided are reviewed before final approval is given.
Borrowing more than needed may hurt your cash flow. If income drops, repayments become difficult. Delays affect your credit score and future loan access. To avoid this, borrow only when needed, track your monthly dues, and limit how many loans you take. A good repayment habit helps avoid long-term stress.
Check the interest charged over time to find the full cost. Add processing fees, late payment charges, etc. Use your EMI amount & loan term to calculate the final outflow.
A few businesses borrow without checking the repayment schedule or hidden charges. Others use instant loans for lengthy financial plans. Always check how repayments impact your monthly income as well as savings.
Companies choose debt financing to keep full control. You borrow money, repay with interest, and continue running your business independently. There's no need to share profits or decision-making rights. Debt financing is often a smarter choice if your business earns steady income and can manage repayments on time.
Download our personal loan app to apply for a personal loan. Get up to 2Lakhs* as a personal loan. Download Now!
Sign into avail a personal loan up to ₹ 2,50,000
Register to avail an instant loan in just a few minutes. Fulfil your financial needs with our loan and repay in easy EMIs.
Apply NowUnifinz Capital India Limited is a Non Banking Finance Company (NBFC) registered with the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). lendingplate is the brand name under which the company conducts its lending operations and specialises in meeting customer’s instant financial needs.
Corporate Identity No. (CIN)
L 1 7 1 1 1 D L 1 9 8 2 P L C 0 1 3 7 9 0
RBI Certificate of Registration No (CoR):
1 4 . 0 0 2 3 3
Registered Office :
Rajlok Building (Floor-5), 24 Nehru Place, New Delhi-110 019

